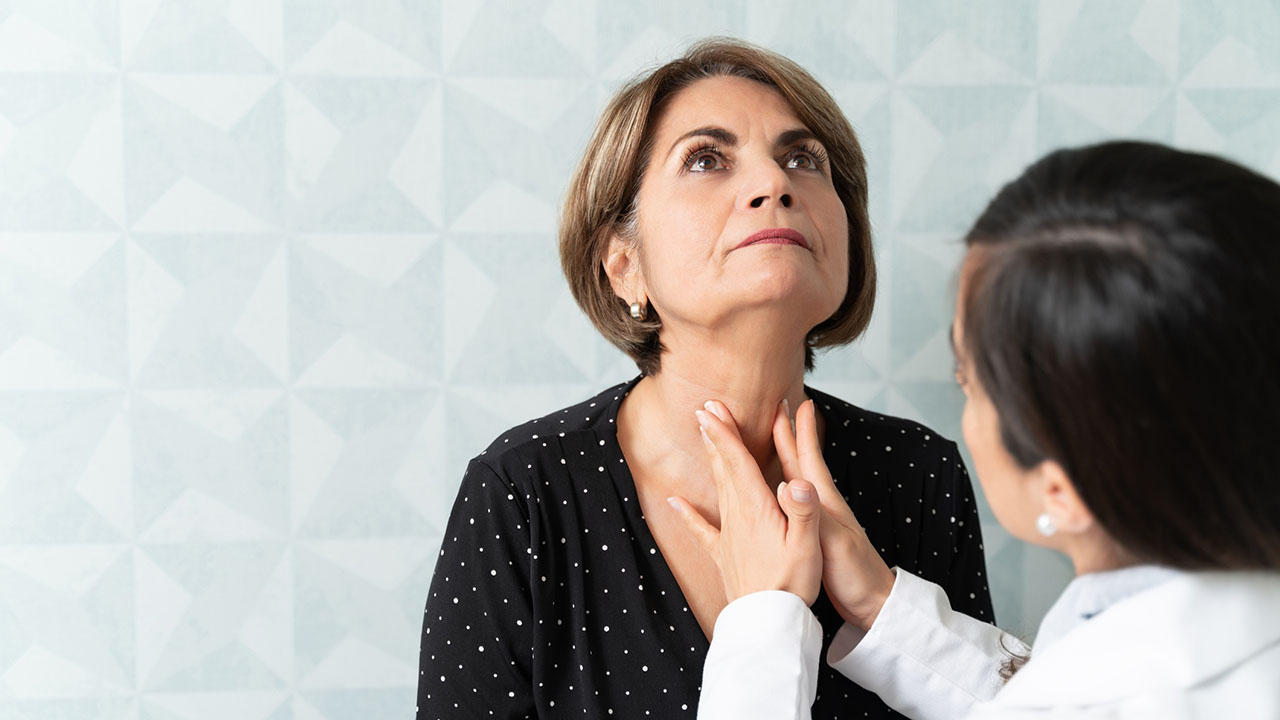


Did you know? Four pea-sized parathyroid glands are located around the thyroid in your neck. While their names are similar, the thyroid and parathyroid glands are completely different. “Para” means “near,” and these glands are part of the endocrine system, which consists of glands that release hormones into the bloodstream. The main function of the parathyroid glands is to make the parathyroid hormone (PTH) to regulate the amounts of calcium, phosphorus and magnesium in your bones and blood.
Calcium is vital to the function of our muscles and nerve cells. The minerals calcium and phosphorus are also important for healthy bones. When calcium levels in the blood are too low, the parathyroid glands release extra PTH, which takes calcium from the bones and stimulates calcium reabsorption in the kidney. If the level of calcium in the blood is too high, the glands reduce hormone production. If your parathyroid glands make too little of these minerals or are enlarged and make too much, it disrupts the balance, resulting in hypoparathyroidism or hyperparathyroidism.
Changing your diet may also be recommended. You may be asked to eat foods high in calcium, such as dairy products, breakfast cereals, fortified orange juice, and green, leafy vegetables. You may also need to avoid eating foods high in phosphorus, such as meat, poultry, fish, nuts, whole grains and beans.
Ready to connect with an ENT specialist?
Find an ENT specialist near you or call (920) 405-1414.
Calcium is vital to the function of our muscles and nerve cells. The minerals calcium and phosphorus are also important for healthy bones. When calcium levels in the blood are too low, the parathyroid glands release extra PTH, which takes calcium from the bones and stimulates calcium reabsorption in the kidney. If the level of calcium in the blood is too high, the glands reduce hormone production. If your parathyroid glands make too little of these minerals or are enlarged and make too much, it disrupts the balance, resulting in hypoparathyroidism or hyperparathyroidism.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis is usually discovered through a blood or urine test to determine PTH, calcium and phosphate levels. Imaging of the neck may be done to further investigate any abnormal parathyroid gland(s) or to help guide any surgical treatment. Such imaging may include ultrasound, nuclear medicine parathyroid scan or four-dimensional CT scan.Hyperparathyroidism:
Symptoms of hyperparathyroidism include:- Muscle spasm
- Bone loss (osteoporosis)
- Kidney disease/stones
- Depression
- Irritability
- Fatigue
- Anxiety
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea or vomiting
Hypoparathyroidism:
Symptoms of hypoparathyroidism include:- A tingling sensation in your fingertips, toes and lips
- Twitching facial muscles
- Muscle pains or cramps, particularly in your legs, feet or tummy
- Fatigue
- Mood changes, such as feeling irritable, anxious or depressed
- Dry, rough skin
- Coarse hair that breaks easily and may fall out
- Fingernails that break easily
Changing your diet may also be recommended. You may be asked to eat foods high in calcium, such as dairy products, breakfast cereals, fortified orange juice, and green, leafy vegetables. You may also need to avoid eating foods high in phosphorus, such as meat, poultry, fish, nuts, whole grains and beans.
Ready to connect with an ENT specialist?
Find an ENT specialist near you or call (920) 405-1414.


.jpg?width=1280&height=720&ext=.jpg)